The world of digital marketing comes with its own vocabulary that is not always familiar to those outside of the industry. It’s important to understand these terms and how they impact your strategy to effectively craft a marketing plan.
We created this glossary of commonly used digital marketing terms to enhance your knowledge and understanding of your center’s marketing efforts!
Social Media
- Ad – A strategic creative used to promote or communicate your brand, product, services, or message.
- Ad Set – An ad set contains one or more ads. You define your targeting, budget, schedule, bidding, and placements at the ad set level.
- Anchor Posts – Anchor posts and filler posts (defined below) make up a social media strategy. While filler posts are meant to garner engagement, anchor posts are meant to educate your audience about your center and services. These are tailored more toward the section of your audience who may be in need of your services.
- Boosted Post – A boosted post is a post to your page’s timeline that you can apply money to in order to show it to an audience of your choosing. Boosted posts differ from Facebook campaigns primarily because they can be easily created directly from the page versus Facebook Ads Manager, but offer less customization than a campaign set up in Ads Manager.
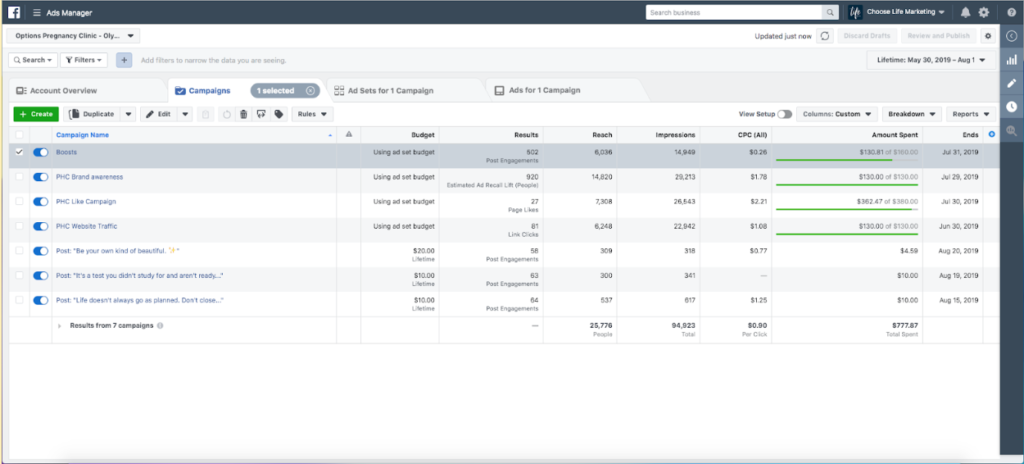
- Campaign – A series of advertising messages that share a theme, and market a product or service. For social, this is where you set your objectives (awareness, traffic, conversions, engagement, etc.)
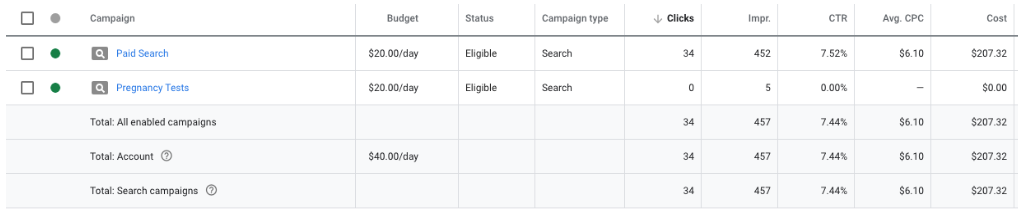
- CPC – Cost-per-click. The amount of money spent for a click on an ad in a campaign. The goal is to get CPC as low as possible. CPC varies greatly across industry, location, audience, ad quality, relevancy and more.
- CTR- Click-through-rate. the ratio of how many times an advertisement was clicked on, versus how many times it was shown. It is calculated by dividing the ad’s clicks by the ad’s impressions. For example, if an ad is shown to 100 people, and 10 of them click the ad, then it has a click through rate of 10% (10 clicks / 100 impressions = 10%)
- Engagement – Social media engagement measures the public shares, likes and comments for an organization’s social media efforts.
- Engagement Rate – Engagement rate is a metric that measures the level of engagement that a piece of created content is receiving from an audience. It shows how much people interact with the content in relation to the number of people who saw your post.
- Filler Posts – Posts that are meant to be engaging and shareable to your target audience, but do not specifically relate to your services, product, or mission. Due to the Facebook and Instagram algorithm favoring engagement, filler posts will help more of your audience see your posts more often instead of posts getting buried in their timelines.
- Hashtag – a phrase beginning with the symbol “#” used in social media as a way for tagging content for users to find. Adding hashtags to a post allows users to find your post when searching for that topic. This can be used for finding users looking for broad topics on social media, as well as niche, detailed topics.
- Impressions – times your content is displayed, regardless of whether it was clicked.
- Organic – a post that does not have any money being used to increase the number of people seeing it. Organic posts are less likely to get seen due to Facebook and Instagram’s pay-to-play algorithm.
- Reach – the total number of people who see your content.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization – The process of improving a website’s performance and positioning in organic search engine results through a variety of methodologies including content production or improvement, technical and code improvement, and link acquisition.
- Alt Text – Alternative text. An attribute added to website code for images, used to provide vision impaired website visitors with information about the contents of a picture. Best practice dictates that all images on a website should have alt text, and that the text should be descriptive of the image.
- Backlink – This is when one website hyperlinks to another website. Backlinks are a major factor used by Google in determining organic rankings.
- Bounce Rate – The percentage of visitors to a website that leave immediately without clicking or interacting with any portion of the page. For example, if 100 people visit a website, and 50 of them immediately leave, the website has a bounce rate of 50%.
- Google My Business – The platform on which businesses can input information to appear in the search results, map packs, location searches, and more. Name, address, phone number, website link, hours of operation, reviews and more can all be managed through this tool. GMB is crucial to local SEO campaigns, and is directly related to location-based searches.
- Google Tag Manager – GTM is a tool that is designed to manage JavaScript and website code tags that are used for tracking and analytics on websites. It allows webmasters and search engine optimizers to add snippets of code and tracking pixels, without having to modify onsite script.
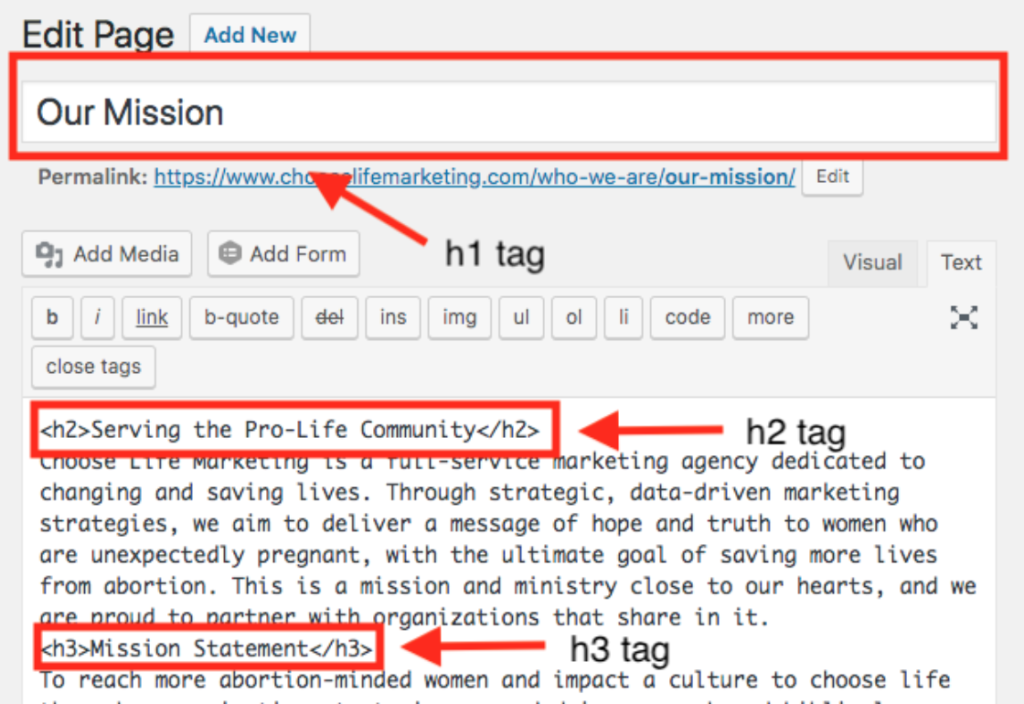
- Header Tags – Header tags are used in website code for categorizing text headings on a web page. They are, in essence, the titles and major topics of a web page and help indicate to readers and search engines what the page is about. Header tags use a cascading format where a page should generally have only one H1 (main title) but beneath can be multiple H2s (subtitles) and every H2 can have H3s beneath (sub-sub titles) and so on.
- Impression – A term used in pay-per-click advertising that represents how many times an ad was shown.
- Keyword – A word or phrase indicative of the major theme in a piece of content. When you search for something in a search engine, you type in a keyword and the search engine gives you results based on that keyword. One major Goal of SEO is to have your website show in searches for as many relevant keywords as possible.
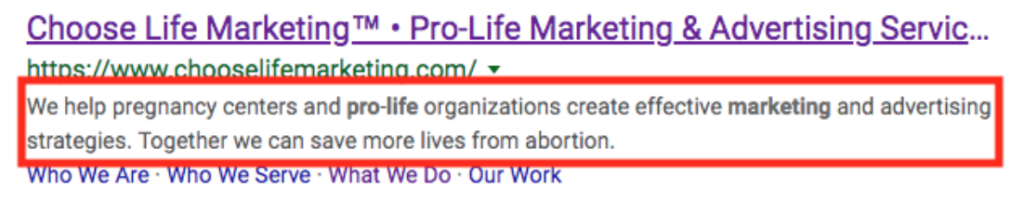
- Meta Description – One of the meta tags that gives a description of the page in 160 characters. The meta description is an important aspect of a webpage because it is what appears in Google searches and other search engine results.
- NAP (name, address, phone number) – An acronym for local citations. Consistency in name, address, and phone number citations is an important piece of a local SEO Campaign. To build local SEO authority, a business’s name, address ,and phone number should be listed across local citation websites like Yelp, Google Business, Angie’s List, Yellow Pages, Better Business Bureau, Foursquare, and more.
- Ranking – A general term for where a website appears on search engine result pages (SERP). A site’s “ranking” may increase or decrease over time for different search terms, or queries. Ranking is specific to each keyword, so a website may have keywords that rank on the first page, and others that don’t.
- Referral – A medium denoted in Google Analytics that represents a website visit that came from another website (as opposed to coming from a Google search, for example). When users click on a link to another, external webpage, they are said to have been “referred” there.
- Title Tag – A website code element that is used to describe the specific topic of a web page. Title tags are displayed in the tabbed top bar of a web browser.
PPC/Remarketing
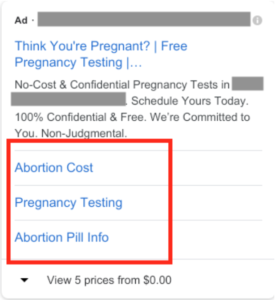
- Ad Extension – Additional pieces of information that can be added to Google Ads ads, including reviews, address, pricing, callouts, app downloads, site links, and click-to-call. Ad extensions help advertisers create richer, more informative ads that take up more on-page real estate, which generally lead to higher Click Through Rates.
- Average Position – A metric in Google Ads that helps advertisers understand where, on average, their ads are showing in Google search results pages. There are usually 4 available ad slots at the top of a search result page (where 1 is the first ad, 2 is the second ad, etc), so for the best results advertisers typically want an average position between 1-4. Average position 5+ indicates that your ads are showing at the bottom of the search results page.
- Bid – placed in a pay-per-click auction to help secure ad placement at the top of search results. Online businesses bid on specific keywords or keyword groups in an attempt to secure ad space for important terms relative to their business.
- Conversion – The completion of a predefined goal. This is often used to track the number of site visitors that have been “converted” to making an appointment, calling in, or making a donation.
- Conversion Rate – The rate at which visitors to a website complete the predefined goal. It is calculated by dividing the number of goal achievements by the total number of visitors. For example, if 100 people visit a website and 10 of them complete the conversion goal (like filling out a contact form) then the conversion rate is 10%.
- CPM – Stands for “Cost Per Thousand” (M is the roman numeral for 1,000). This is the amount an advertiser pays for 1,000 impressions of their ad. For example, if a publisher charges $10 CPM, and your ad shows 2000 times, you will pay $20 for the campaign ($10 x 1000 impressions) x 2. Measuring ad success with CPM is most common in awareness campaigns, where impressions are more important than conversions or clicks.
- Display Ads – Ads on a display network which include many different formats such as: images, flash, video, and audio. When it comes to offline ads it is important that you understand banner buying guide. But here the display ads are commonly known as banner ads, these are the advertisements that are seen around the web on news sites, blogs, and social media.
- Google Ads (formerly Google AdWords) – Google’s online advertising service. This system allows advertisers to reach customers through their search and display networks. Google Ads offers several cost models which vary by bidding strategy and company goals. Advertisers can bid on keywords which allows their ads to show in Google search results and on Google’s network of partner websites.
- Google Analytics – A free software platform created by Google, which is used to analyze nearly every aspect of users accessing a website. Website traffic, conversions, user metrics, historical data comparisons, and effectiveness of each channel of marketing can all be managed using this tool.
- Google Grant – A donation program that distributes free in-kind advertising to select 501(c)(3) nonprofit organizations.
- Google Search Console – Search Console is a free tool Google offers to webmasters. Within the tool are several areas that include data on how a site is performing in search. Search Console differs from Analytics – it does not measure traffic, it measures a site’s visibility on search pages, and indexability. Metrics Search Console measures are: Click-through rate, number of indexed pages, number of dead links (AKA 404 pages), and more. (See also: Google Analytics, Click-through rate, Index, Crawler/Spider)
- Google Search Network – A group of search-related websites and apps where your ads can appear. When you advertise on the Google Search Network, your ad can show near search results when someone searches with terms related to one of your keywords.
- Landing Page – The destination webpage a user lands on after clicking on a link (either in an ad or elsewhere). Some landing pages are designed with the purpose of lead generation, while others are used to direct the flow of traffic throughout a site.
- Lead – A potential client who gave you their information.
- Negative Keyword – Negative keywords let you exclude search terms from your campaigns and help you focus on only the keywords that matter to your customers. Better targeting can put your ad in front of interested users and increase your return on investment
- PPC – Pay-per-click. An online advertising model in which advertisers are charged for their ad once it is clicked. The PPC model is commonly associated with search engine and social media advertising like Google Ads and Facebook Ads.
- Quality Score – Google Ads rating of the relevance and quality of keywords used in PPC campaigns. These scores are largely determined by relevance of ad copy, expected click-through rate, as well as the landing page quality and relevance. Quality score is a component in determining ad auctions, so having a high score can lead to higher ad rankings at lower costs.
- Remarketing – Also known as retargeting, a type of paid ad that allows advertisers to show ads to customers who have already visited their site. Once a user visits a site, a small piece of data called a “cookie” will be stored in the user’s browser. When the user then visits other sites, this cookie can allow remarketing ads to be shown. Remarketing allows advertisers to “follow” users around in attempts to get the user back to the original site.
- Total clicks – The total amount of times your ad was clicked on
- Unique clicks – The total amount of different IP addresses/devices clicked on your ad
Website
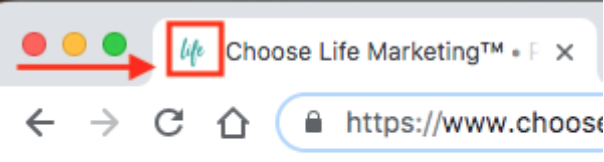
- Favicon – an icon associated with a URL that is variously displayed, as in a browser’s address bar or next to the site name in a bookmark list.
- Heatmap – A heatmap illustrates how users interact with your site. This tracks where users click and hover over so you can optimize your design.
- Hyperlink (or link) – A hyperlink creates a link from one webpage to another web page, characterized often by a highlighted word or image that takes you to the destined location when you click on that highlighted item.
- Responsive Design – Mobile friendly. A philosophy of creating a website that allows all of the content to show correctly regardless of screen size or device. Your website will “respond” to the size of the screen each user has, shrinking and reorganizing on smaller screens, and expanding to fill appropriately on large ones.
- SSL – A secure way of transferring data over the internet, such as personal information and credit card transactions. It can be compared to sending a sealed envelope that only the recipient can open, rather than a postcard that anyone who comes in contact with it can read.
- Unique visitor – Tracks how many different people visit your website. Unique visitors are tracked by their IP addresses. If a visitor visits the same website multiple times, they will only be counted once in the unique visitors metric.
- URL – stands for Uniform Resource Locator and is the address of a web page. The URL refers to what specific web page a web browser is viewing. https://www.chooselifemarketing.com is an example of a URL.
Knowing the language that is used to explain digital marketing tactics and features can be extremely helpful in giving you a cohesive and holistic view of your center’s marketing efforts. It allows you to understand each tactic and how it contributes to your center’s greater goals.
We hope that this digital marketing term glossary empowers you to feel more confident when discussing your digital marketing strategies. If you want to learn more about how Choose Life Marketing can enhance your center’s marketing efforts, contact us today!
Give us a call at 573-445-9295, email us at info@chooselifemarketing.com, or visit our website at www.chooselifemarketing.com to learn more about how we can help!